Raven

Introduction
The Raven is a majestic species of rugged uplands, highly intelligent and steeped in mythology. It is the UK's largest crow.
The size of a Buzzard, the Raven is a strong flier, regularly performing tumbling aerobatics in flight. Its all-dark plumage, heavy bill and diamond-shaped tail are distinctive, as is its harsh, evocative 'kronk-kronk-kronk' call. Paired birds are territorial and will chase away interlopers. The species feeds mainly on carrion.
The Raven is a relatively early breeder, laying four to six eggs from February to April. Following a decline and numbers contraction in this species' range towards the west in the 20th century, the UK population has since risen again and the range has been extending eastwards once more.
- Our Trends Explorer gives you the latest insight into how this species' population is changing.

Key Stats
Identification
ID Videos
This section features BTO training videos headlining this species, or featuring it as a potential confusion species.
Corvids
Songs and Calls
Call:
Status and Trends
Conservation Status
Population Change
Between the 1968-72 and 1988-91 atlas periods, the Raven's range contracted from some areas of Scotland and northern England. Declines in southern Scotland and northern England were associated with large-scale afforestation (Marquiss et al. 1978), while closer sheep husbandry and conversion of pasture to arable were also implicated (Mearns 1983). A thorough survey of northwest Wales during 1998 to 2005 found at least 69% more nesting pairs than a previous survey of the same area during 1978-85 and evidence of an increase of 173% since around 1950, at a rate that accelerated after 1990 (Driver 2006). Using data from the Scottish Raptor Monitoring Scheme and Bird Atlas 2007-11, produced an estimate of 3,241 (1,035-5,447) breeding pairs across Scotland (Wilson et al. 2019).
Ravens have increased along the English-Welsh border and colonised extensive new areas of the south coast, western and midland England and southern Scotland since 1988-91 (Cross 2002, Balmer et al. 2013). BBS indicates overall increase in England and Scotland since 1995 and stability in Wales over the same period. Nest success appears to have improved slightly, although the number of fledglings per breeding attempt is unchanged. There has been a widespread increase across Europe since 1980 (PECBMS: PECBMS 2020a>): increases are evident in all regions but have been weakest in the south and west, including UK (PECBMS 2009).
Distribution
The Raven is now as much a bird of pastoral or mixed lowland farmland and forestry as it is of the uplands, having expanded eastwards over recent decades, although densities remain highest in those regions in the north and west of Britain and upland and coastal Ireland that formed the strongholds before the recent range expansion.
Occupied 10-km squares in UK
2007/08–10/11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
2008–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
European Distribution Map
Distribution Change
The Raven's British & Irish range has expanded by 79% in winter and by 68% in the breeding season since the 1981–84 Winter Atlas and 1968–72 Breeding Atlas, respectively.
Change in occupied 10-km squares in the UK
from 1981–84 to 2007–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
from 1968–72 to 2008–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
Seasonality
Raven is recorded throughout the year on up to 20% of complete lists.
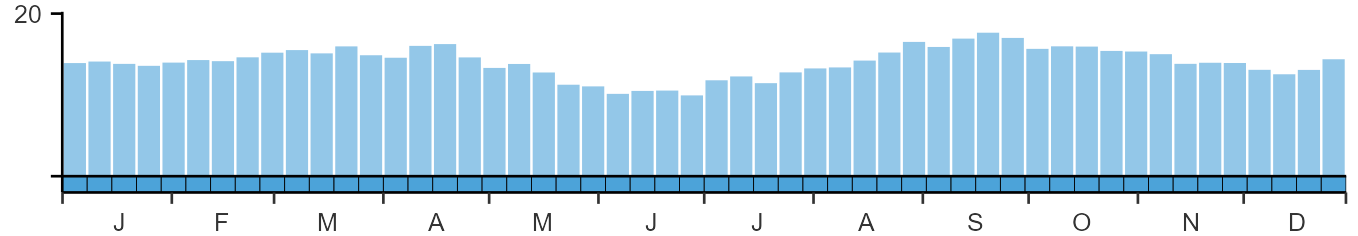
Weekly pattern of occurrence
The graph shows when the species is present in the UK, with taller bars indicating a higher likelihood of encountering the species in appropriate regions and habitats.
Habitats
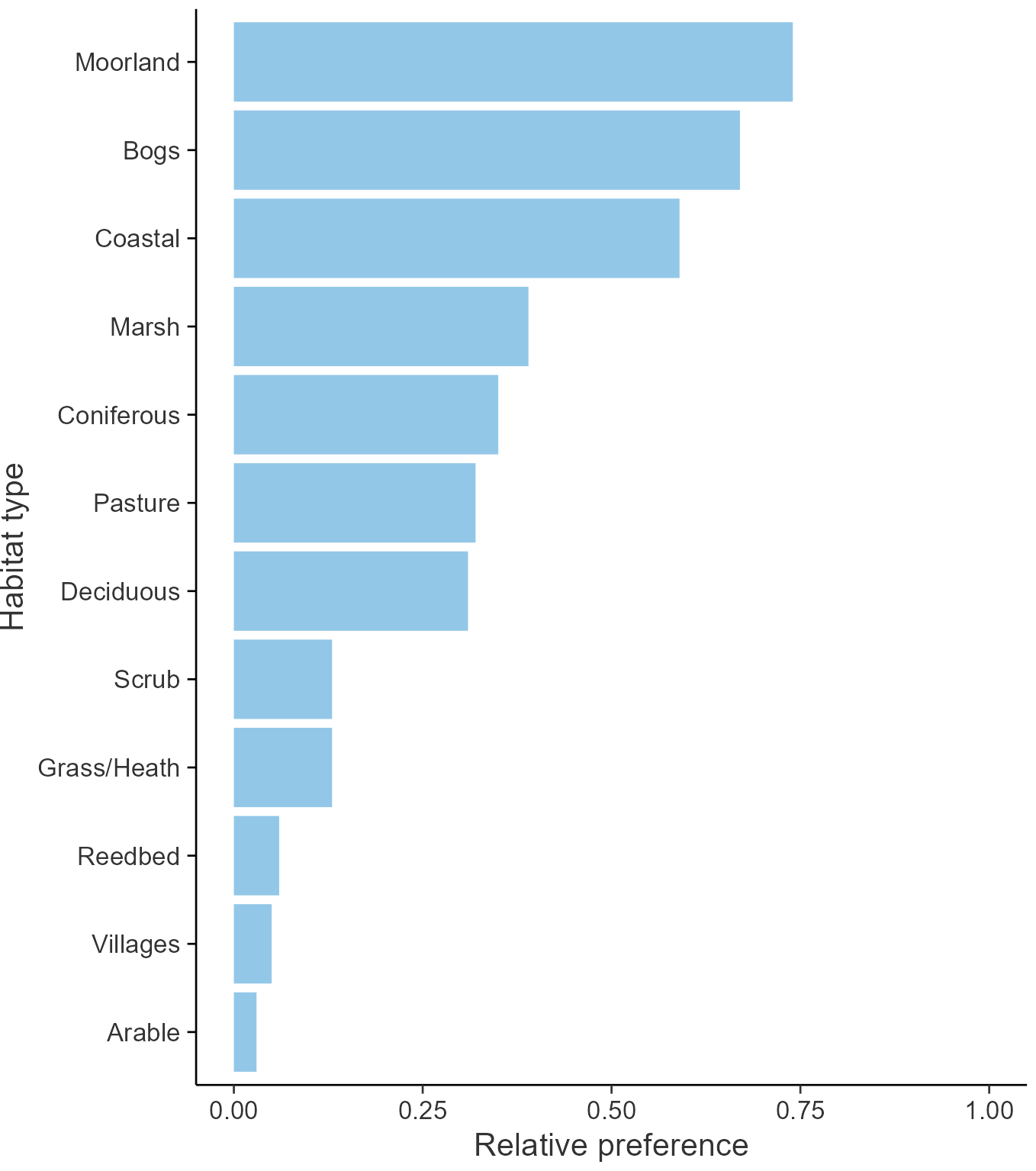
Breeding season habitats
Relative frequency by habitat
The graph shows the habitats occupied in the breeding season, with the most utilised habitats shown at the top. Bars of similar size indicate the species is equally likely to be recorded in those habitats.
Movement
Britain & Ireland movement
Foreign locations of birds ringed or recovered in Britain & Ireland
Dots show the foreign destinations of birds ringed in Britain & Ireland, and the origins of birds ringed overseas that were subsequently recaptured, resighted or found dead in Britain & Ireland. Dot colours indicate the time of year that the species was present at the location.
- Winter (Nov-Feb)
- Spring (Mar-Apr)
- Summer (May-Jul)
- Autumn (Aug-Oct)

European movements
EuroBirdPortal uses birdwatcher's records, such as those logged in BirdTrack to map the flows of birds as they arrive and depart Europe. See maps for this species here.
The Eurasian-African Migration Atlas shows movements of individual birds ringed or recovered in Europe. See maps for this species here.
Biology
Productivity and Nesting
Nesting timing
Egg measurements
Clutch Size
Incubation
Fledging
Survival and Longevity
Survival is shown as the proportion of birds surviving from one year to the next and is derived from bird ringing data. It can also be used to estimate how long birds typically live.
View number ringed each year in the Online Ringing Report.
Lifespan
Biometrics
Wing length and body weights are from live birds (source).
Ring Size
Classification, names and codes
Classification and Codes
- Order: Passeriformes
- Family: Corvidae
- Scientific name: Corvus corax
- Authority: Linnaeus, 1758
- BTO 2-letter code: RN
- BTO 5-letter code: RAVEN
- Euring code number: 15720
Alternate species names
- Catalan: corb comú
- Czech: krkavec velký
- Danish: Ravn
- Dutch: Raaf
- Estonian: ronk e. kaaren
- Finnish: korppi
- French: Grand Corbeau
- Gaelic: Fitheach
- German: Kolkrabe
- Hungarian: holló
- Icelandic: Hrafn
- Irish: Fiach Dubh
- Italian: Corvo imperiale
- Latvian: krauklis
- Lithuanian: paprastasis kranklys
- Norwegian: Ravn
- Polish: kruk (zwyczajny)
- Portuguese: corvo
- Slovak: krkavec cierny
- Slovenian: krokar
- Spanish: Cuervo grande
- Swedish: korp
- Welsh: Cigfran
Research
Causes of Change and Solutions
Causes of change
There is little good evidence available regarding the drivers of the breeding population change in this species in the UK.
Further information on causes of change
Historical decreases in Raven numbers across the UK occurred but the population has increased again during from the mid-twentieth century and the species has reoccupied much of its former range. This has bought it into conflict with people due to concerns about damage to livestock. Adult survival rates and breeding productivity have increased over time, and the consequent population recovery was most likely aided by reduced persecution; ringing recovery information suggests that the frequency of illegal killing may have declined in the twenty-first century, although this finding should be treated with caution as another possible interpretation is that ringed birds which have been shot and poisoned birds are now less likely to be reported. Recent increases in licensed control have occurred in Scotland, and a report investigating population dynamics has therefore been carried out in order to assess the effects of control on Scottish raven populations (Wilson et al. 2019).
Information about conservation actions
The Raven has been increasing and expanding its range in the UK over the last 30 years and therefore is not currently a species of conservation concern. However, there are also concerns that illegal control may be occurring (see Causes of Change section, above) which could have local population level impacts in some areas.
This species causes conflict with farmers due to concerns about damage to livestock and legal control now occurs in Scotland. There are also concerns about the possible impact of Raven populations on other native species such as upland waders. For example, a study looking at the UK uplands found no significant spatial or temporal relationships which could justify lethal control of Ravens between any of the five species of waders studied, but did find near significant relationships with curlew and lapwing trends, which the authors suggested merited further investigation (Amar et al. 2010b).
To ensure that the conservation status of this species remains unchanged and that the recent gains are not reversed, any policy decisions about the legal control of Ravens, whether for economic reasons or in order to benefit other native species, should be based on scientific evidence. A review in Scotland used population modelling to assess the effects of licenced control of Raven and define levels of control that are likely to be 'sustainable' (Wilson et al. 2019). They concluded that the maximum level of 'sustainable' control (i.e. control that will not result in long-term decline) is around 200 non-breeding Ravens per 100 x 100 km square in Scotland. However, they caution that this figure is subject to uncertainty around some of the information input into the model and to variation in aspects such as adult survival rates and breeding densities; hence the level of sustainable control may be lower in some areas and further understanding of Raven movements and breeding ecology is needed. Further research is also still be required in order to make evidence-based decisions about control in order to benefit other native species (e.g. research into the possible effects of Ravens on Curlews and Lapwings).
Publications (2)
Watching Out for Waders: The Working for Waders Nest Camera Project
Author:
Published: 2024
This report presents the results of a trial involving the use of trail cameras by land managers and other wader conservation stakeholders to monitor the outcome of wader nesting attempts. It presents the results of the trial and assesses the potential for the project to improve wader conservation knowledge and management.
04.10.24
BTO Research Reports

Associations between gamebird releases and general predators
Author:
Published: 2019
BTO research reveals that the release of Pheasants and Red-legged Partridges for commercial shoots may be boosting numbers of the avian predators and scavengers. Every year, 41-50 million non-native gamebirds (Pheasant and Red-legged Partridge) are released in the UK. Fewer than half these birds are shot, meaning there is potentially a large food resource available to predators and scavengers, sustaining their populations above the levels they would otherwise reach. If it occurs, this inflation of predator numbers might alter predator-prey dynamics, increasing predation pressure on some vulnerable species, including declining breeding waders like Curlew. This study used data from the Breeding Bird Survey and Bird Atlas 2007-11 to identify associations between the occurrence patterns of gamebirds and the abundance and population growth rates of several generalist predators, including Buzzard, Jay, Raven, Magpie and crows (Carrion and Hooded combined). While many other factors influence predator abundance, such as fine-scale habitat variation, availability of other food sources, and game management activities, the results suggest that large-scale variation in avian predator populations is predominantly positively affected by gamebird releases. The potential implications of this finding need to be thoroughly tested. Such tests could include regulation of releases on a trial basis, to determine effects on ground nesting birds, for example. The compulsory recording of releases and the number of predators controlled would also be valuable for a better understanding of the impacts, positive or negative, of gamebird releases on the wider environment. Read a blog post by publication author Henrietta Pringle discussing the work behind this paper.
02.07.19
Papers

More Evidence
More evidence from Conservation Evidence.com
Partners
Citing BirdFacts
If you wish to cite particular content in this page (e.g. a specific value) it is best to use the original sources as linked in the page. For a more general citation of the whole page please use: BTO (20XX) BirdFacts Species: profiles of birds occurring in the United Kingdom. BTO, Thetford (www.bto.org/birdfacts, accessed on xx/xx/xxxx).