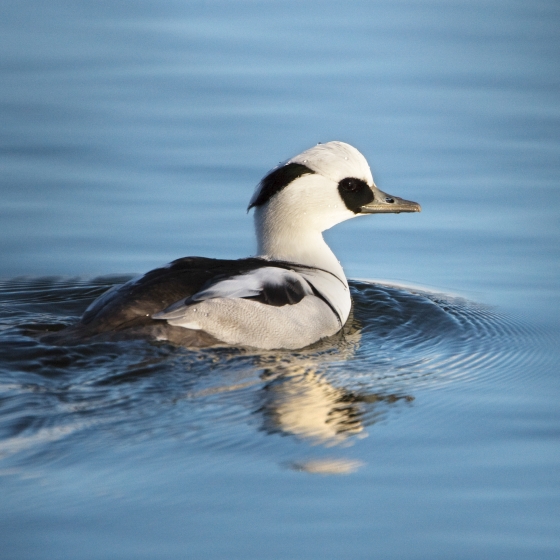
Smew

Introduction
Crisp black and white-coloured male and red-headed female Smew are winter visitors to UK lakes, reservoirs and coastal waters.
Smew begin arriving in the UK during October but have a prolonged period of movements throughout the winter and birds can arrive at any time in response to freezing conditions on their Continental wintering areas. The south-east of the UK receives the lion's share but a few individuals do make it further west. Records are scarce in Scotland, Wales and Ireland.
The numbers of Smew wintering in the UK has fallen in recent years, possibly in response to milder conditions on the Continent, which maintain waterbodies free of ice for longer.

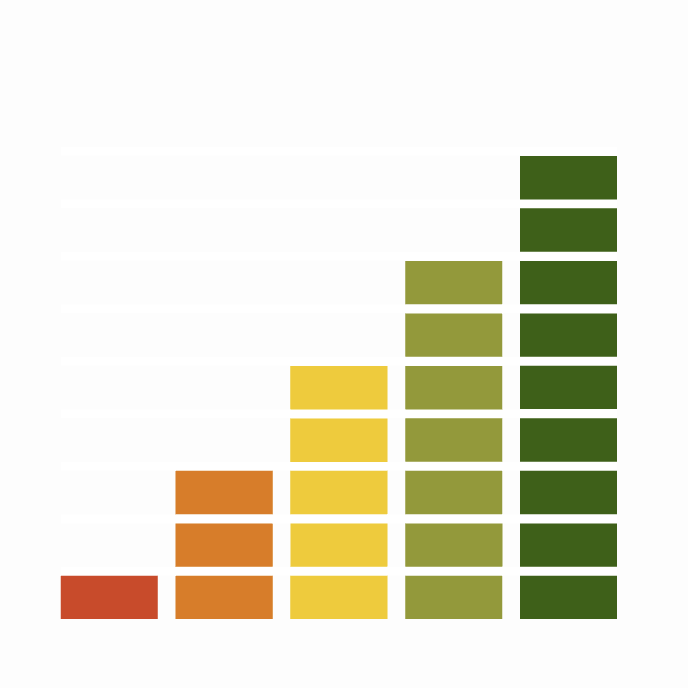
Key Stats
Status and Trends
Conservation Status
Population Size
Population Change
Although there are occasional records of individual Smew in the UK in the summer months, it is primarily a winter visitor; recent estimates show the winter population to comprise approximately 130 individuals Frost et al. 2019]. The species is found across lowland areas of England, Scotland and Wales, with numbers increasing in colder winters when small influxes occur as birds escape colder conditions on the Continent [Balmer et al. 2013]. It is a species that is strongly associated with gravel pit complexes with the majority of the wintering population found in this habitat [Austin et al. 2014]. [WeBS data show that numbers peaked in the the mid-1990s, since when they have declined sharply.
Distribution
The Smew's winter distribution map shows that they were recorded widely across lowland England, Scotland and Wales during 2007–11. There were also records from the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands, where they are scarce winter visitors.
Occupied 10-km squares in UK
2007/08–10/11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
2008–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
European Distribution Map
Distribution Change
Change in occupied 10-km squares in the UK
from 1981–84 to 2007–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
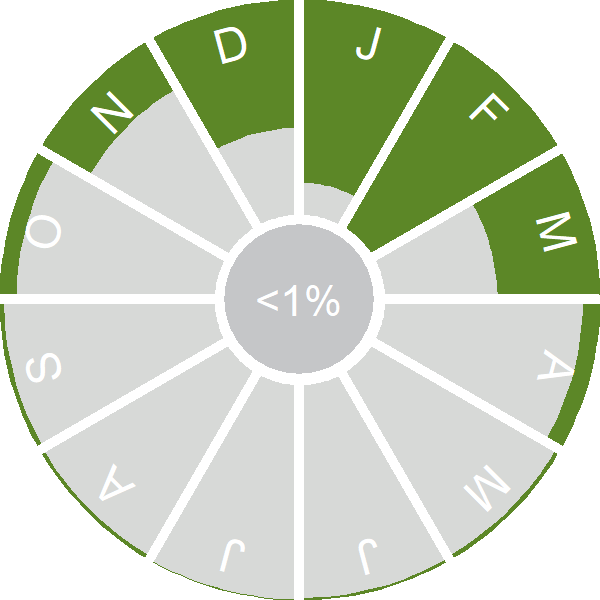
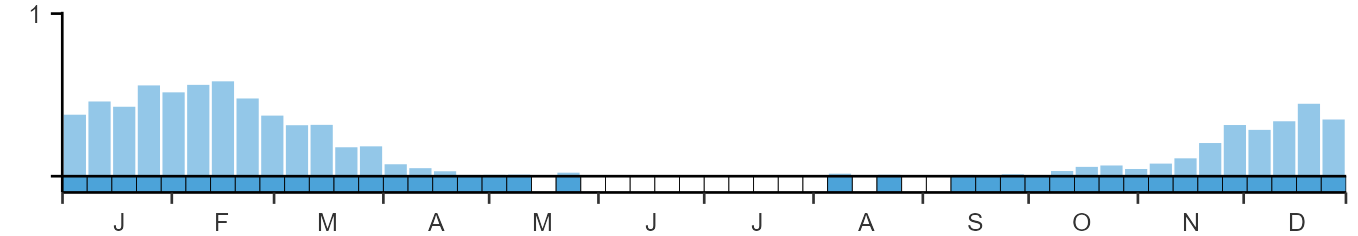
Seasonality
Smews are localised winter visitors, most often recorded in late winter when cold weather on the continent can push birds into southern Britain.
Weekly pattern of occurrence
The graph shows when the species is present in the UK, with taller bars indicating a higher likelihood of encountering the species in appropriate regions and habitats.
Movement
Britain & Ireland movement
European movements
EuroBirdPortal uses birdwatcher's records, such as those logged in BirdTrack to map the flows of birds as they arrive and depart Europe. See maps for this species here.
The Eurasian-African Migration Atlas shows movements of individual birds ringed or recovered in Europe. See maps for this species here.
Biology
Productivity and Nesting
Nesting timing
Egg measurements
Clutch Size
Fledging
Survival and Longevity
Survival is shown as the proportion of birds surviving from one year to the next and is derived from bird ringing data. It can also be used to estimate how long birds typically live.
Classification, names and codes
Classification and Codes
- Order: Anseriformes
- Family: Anatidae
- Scientific name: Mergellus albellus
- Authority: Linnaeus, 1758
- BTO 2-letter code: SY
- BTO 5-letter code: SMEW.
- Euring code number: 2200
Alternate species names
- Catalan: bec de serra petit
- Czech: morcák malý
- Danish: Lille Skallesluger
- Dutch: Nonnetje
- Estonian: väikekoskel e. pudukoskel
- Finnish: uivelo
- French: Harle piette
- Gaelic: Sìolta-bhreac
- German: Zwergsäger
- Hungarian: kis bukó
- Icelandic: Hvítönd
- Irish: Síolta Gheal
- Italian: Pesciaiola
- Latvian: maza gaura, duncka
- Lithuanian: mažasis danciasnapis
- Norwegian: Lappfiskand
- Polish: bielaczek
- Portuguese: merganso-pequeno
- Slovak: potápac malý
- Slovenian: mali žagar
- Spanish: Serreta chica
- Swedish: salskrake
- Welsh: Lleian Wen
- English folkname(s): White Nun (m) Redhead (f)
Research
Causes of Change and Solutions
Causes of change
Several species of diving ducks have shifted their wintering range in a more north-easterly direction over the past three decades due to an increase of 3.8°C in the north-eastern part of the wintering range in early winter [Lehikoinen et al. 2013]. The reduction of Smew numbers in the UK is thought to be a related to this shift, as evidenced by the increase in Smew in Sweden from 400 birds in 1971 to 3,800 in 2004 [Nilsson 2008].
Publications (2)
The status of our bird populations: the fifth Birds of Conservation Concern in the United Kingdom, Channel Islands and Isle of Man and second IUCN Red List assessment of extinction risk for Great Britain
Author:
Published: 2021
Commonly referred to as the UK Red List for birds, this is the fifth review of the status of birds in the UK, Channel Islands and Isle of Man, published in December 2021 as Birds of Conservation Concern 5 (BOCC5). This updates the last assessment in 2015. Using standardised criteria, experts from a range of bird NGOs, including BTO, assessed 245 species with breeding, passage or wintering populations in the UK and assigned each to the Red, Amber or Green Lists of conservation concern. The same group of experts undertook a parallel exercise to assess the extinction risk of all bird species for Great Britain (the geographical area at which all other taxa are assessed) using the criteria and protocols established globally by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This resulted in the assessment of 235 regularly occurring species (breeding or wintering or both), the total number assessed differing slightly from BOCC5 due to different rules on the inclusion of scarce breeders and colonisation patterns. The results of this second IUCN assessment (IUCN2) are provided in the same paper as BOCC5. Increasingly at risk This update shows that the UK’s bird species are increasingly at risk, with the Red List growing from 67 to 70. Eleven species were Red-listed for the first time, six due to worsening declines in breeding populations (Greenfinch, Swift, House Martin, Ptarmigan, Purple Sandpiper and Montagu’s Harrier), four due to worsening declines in non-breeding wintering populations (Bewick’s Swan, Goldeneye, Smew and Dunlin) and one (Leach’s Storm-petrel) because it is assessed according to IUCN criteria as Globally Vulnerable, and due to evidence of severe declines since 2000 based on new surveys on St Kilda, which holds more than 90% of the UK’s populations. The evidence for the changes in the other species come from the UK’s key monitoring schemes such as BTO/JNCC/RSPB Breeding Bird Survey (BBS) for terrestrial birds, the BTO/RSPB/JNCC Wetland Bird Survey (WeBS) for wintering populations and the Rare Breeding Bird Panel (RBBP) for scarce breeding species such as Purple Sandpiper. The IUCN assessment resulted in 108 (46%) of regularly occurring species being assessed as threatened with extinction in Great Britain, meaning that their population status was classed as Critically Endangered, Endangered, or Vulnerable, as opposed to Near Threatened or of Least Concern. Of those 108 species, 21 were considered Critically Endangered, 41 Endangered and 46 Vulnerable. There is considerable overlap between the lists but unlike the Red List in BOCC5, IUCN2 highlights the vulnerability of some stable but small and hence vulnerable populations as well as declines in species over much shorter recent time periods, as seen for Chaffinch and Swallow.
01.12.21
Reports Birds of Conservation Concern

The risk of extinction for birds in Great Britain
Author:
Published: 2017
The UK has lost seven species of breeding birds in the last 200 years. Conservation efforts to prevent this from happening to other species, both in the UK and around the world, are guided by species’ priorities lists, which are often informed by data on range, population size and the degree of decline or increase in numbers. These are the sorts of data that BTO collects through its core surveys. For most taxonomic groups the priority list is provided by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) – the IUCN Red List comprises roughly 12,000 species worldwide and their conservation status. However, for birds in the UK, most policy makers refer to the Birds of Conservation Concern (BoCC) list, updated every six years (most recently in 2015). A new study funded by the RSPB and Natural England in cooperation with BTO, WWT, JNCC, and Game & Wildlife Trust has carried out the first IUCN assessment for birds in Great Britain. The study applied the IUCN criteria to existing bird population data obtained from datasets like the BTO/JNCC/RSPB Breeding Bird Survey (BBS). The criteria take into account various factors, most notably any reduction in the size (both in abundance and range) of populations, loss of habitats key to the species, small or vulnerable population sizes, and extinction risk. Alongside this, the criteria look to see if there is a “rescue” effect – such as immigration from neighbouring populations that might boost the population’s numbers, reducing the risk of extinction. The species are then categorised into one of the threat levels below. The results of the new study show that a concerning 43% of regularly occurring species in Great Britain are classed as Threatened, with another 10% classified as Near Threatened. Twenty-three breeding or non-breeding populations of birds were classed as Critically Endangered, including Fieldfare and Golden Oriole (both possibly extinct as breeders), Whimbrel, Turtle Dove, Arctic Skua and Kittiwake, as well as non-breeding populations of Bewick’s Swan, White-fronted Goose and Smew., Over the past 200 years, seven species have gone extinct as breeders in Britain, including Serin, Temminck’s Stint and Wryneck in the past 25 years. The total percentage of threatened birds in Great Britain (43%) is high compared to that seen elsewhere in Europe (13%). Reasons for this are not entirely clear, although it may be that Britain’s island status has something to do with this, as there are fewer neighbouring “rescue” populations. Although the results from the IUCN assessment and BoCC assessment largely overlap, the IUCN assessment raises the level of concern for species such as Red-Breasted Merganser, Great Crested Grebe, Moorhen, Red-Billed Chough (all classed as Vulnerable), and Greenfinch (Endangered). These species might thus warrant closer monitoring in the near future. In contrast, the BoCC assessment identifies a number of species of concern whose declines have been more gradual but over long time periods (e.g. Skylark and House Sparrow). The authors emphasise that this assessment is not a replacement of the BoCC report, but rather that the two reports complement each other. With this new wealth of knowledge, there will hopefully be even more support for those species that need it most.
01.09.17
Papers

More Evidence
More evidence from Conservation Evidence.com
Partners
Citing BirdFacts
If you wish to cite particular content in this page (e.g. a specific value) it is best to use the original sources as linked in the page. For a more general citation of the whole page please use: BTO (20XX) BirdFacts Species: profiles of birds occurring in the United Kingdom. BTO, Thetford (www.bto.org/birdfacts, accessed on xx/xx/xxxx).