Great Black-backed Gull

Introduction
This impressive gull can be seen at coastal locations throughout the year, but it is less commonly encountered at inland sites.
Although Great Black-backed Gulls breed at coastal sites around much of our coast, they are absent from most of the North Sea coast. The highest breeding season densities are to be found around the Northern Isles, north-west Scotland and the Atlantic coast of south-west Ireland.
The pronounced pattern of winter abundance, which is greatest in the eastern half of Britain, underlines the arrival of wintering individuals from Scandinavia. Ringing data link these birds with populations in Norway and Sweden.

Key Stats
Identification
ID Videos
This section features BTO training videos headlining this species, or featuring it as a potential confusion species.
Adult black-backed gulls
Songs and Calls
Alarm call:
Flight call:
Status and Trends
Conservation Status
Population Change
Numbers of Great Black-backed Gull remained relatively stable between the 1969–70 Census and Seabird 2000 (1998–2002), with a very shallow decline of 11% (JNCC 2022). Since Seabird 2000, annual monitoring suggests that this shallow decline may have continued although this is uncertain due to wide confidence limits and the recent trend may be stable: the latest Census results (2015–2021) may help clarify the trend once they are available (JNCC 2022). The Great Black-backed Gull remains almost exclusively a coastal-breeding species, although a very small number of pairs have been recorded at inland colonies (Balmer et al. 2013).
Distribution
Wintering Great Black-backed Gulls occur all around the coast of Britain & Ireland, as well as at inland, lowland sites in England and Scotland. Breeding birds have a predominantly coastal distribution around both Britain and Ireland, though they are largely absent from most of the North Sea coast between Lothian and Kent.
Occupied 10-km squares in UK
2007/08–10/11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
2008–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
European Distribution Map
Distribution Change
There has been a substantial 30% range contraction in Ireland since the 1968–72 Breeding Atlas, though much of this loss occurred between 1968–72 and 1988–91. A recent contraction is apparent in western Scotland but is outweighed by gains elsewhere in Britain, especially along the English south coast. Since the 1988–91 Breeding Atlas there has been a 7% increase in the number of 10-km squares occupied in Britain & Ireland.
Change in occupied 10-km squares in the UK
from 1981–84 to 2007–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
from 1968–72 to 2008–11
or view it on Bird Atlas Mapstore.
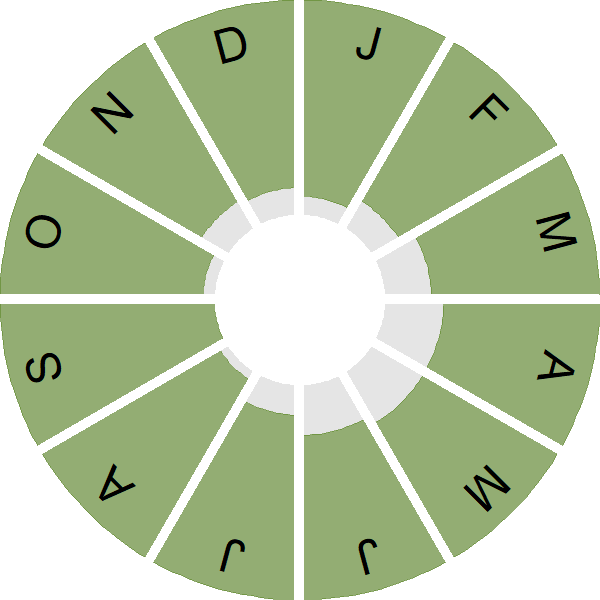
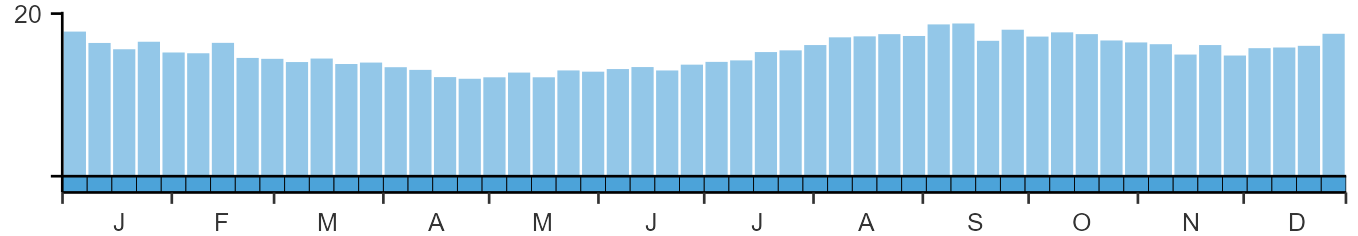
Seasonality
Great Black-backed Gulls are recorded throughout the year.
Weekly pattern of occurrence
The graph shows when the species is present in the UK, with taller bars indicating a higher likelihood of encountering the species in appropriate regions and habitats.
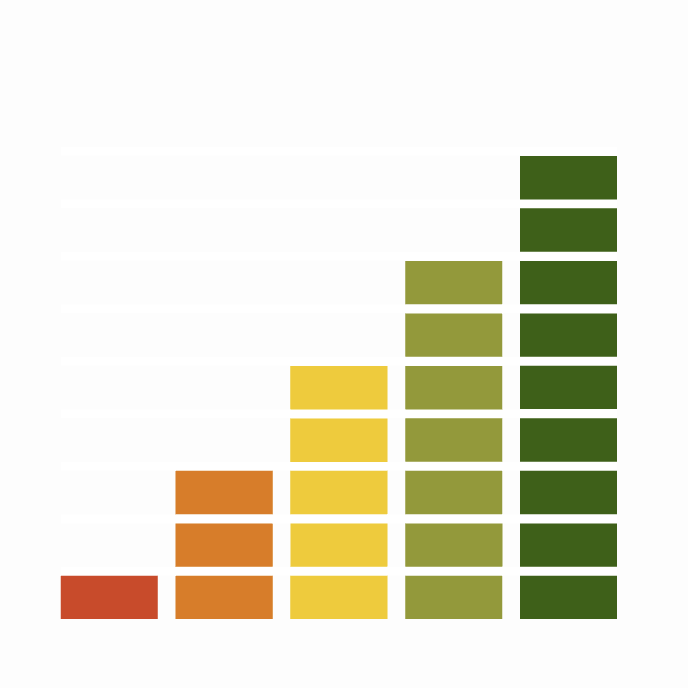
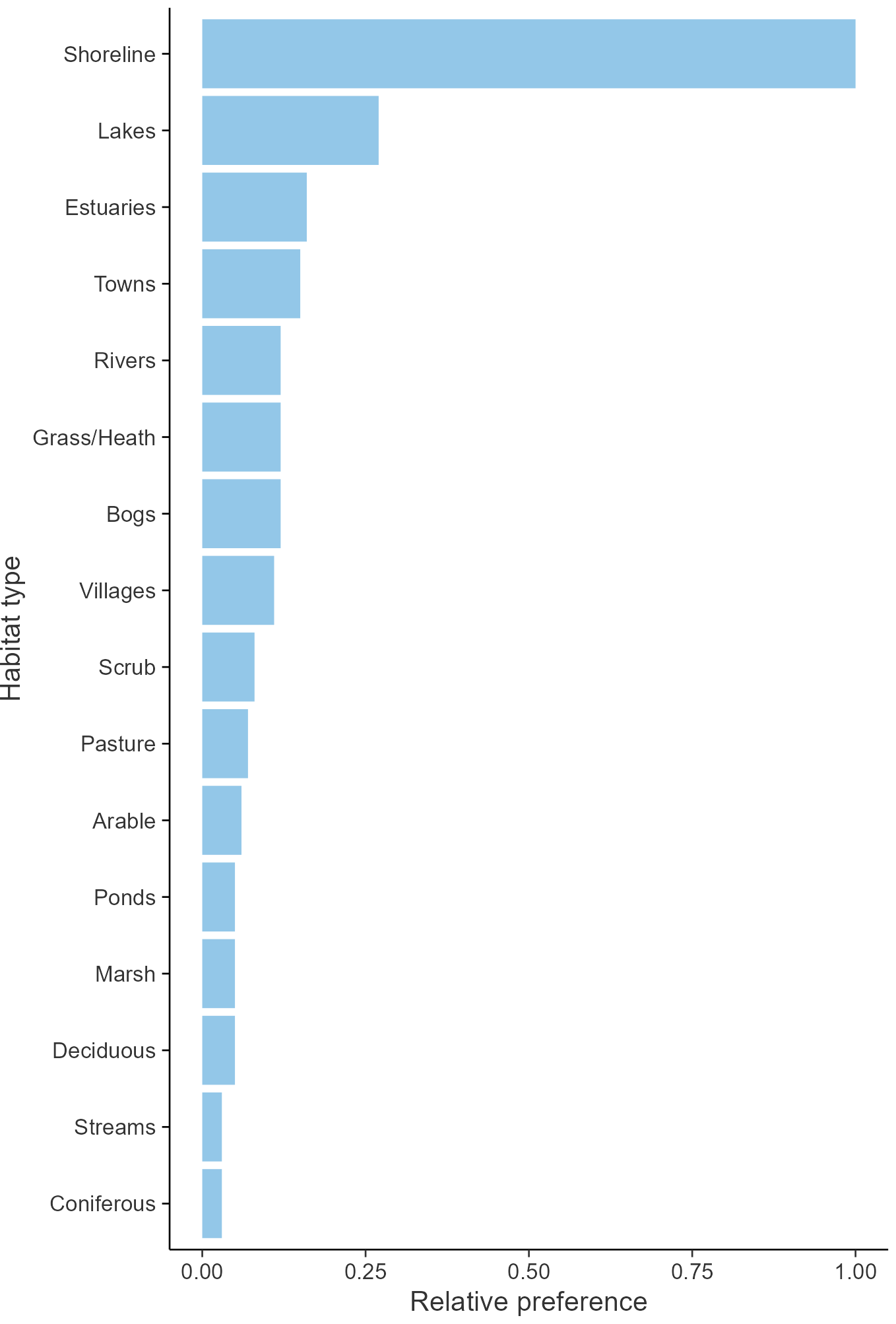
Habitats
Breeding season habitats
Relative frequency by habitat
The graph shows the habitats occupied in the breeding season, with the most utilised habitats shown at the top. Bars of similar size indicate the species is equally likely to be recorded in those habitats.
Movement
Britain & Ireland movement
Foreign locations of birds ringed or recovered in Britain & Ireland
Dots show the foreign destinations of birds ringed in Britain & Ireland, and the origins of birds ringed overseas that were subsequently recaptured, resighted or found dead in Britain & Ireland. Dot colours indicate the time of year that the species was present at the location.
- Winter (Nov-Feb)
- Spring (Mar-Apr)
- Summer (May-Jul)
- Autumn (Aug-Oct)

European movements
EuroBirdPortal uses birdwatcher's records, such as those logged in BirdTrack to map the flows of birds as they arrive and depart Europe. See maps for this species here.
The Eurasian-African Migration Atlas shows movements of individual birds ringed or recovered in Europe. See maps for this species here.
Biology
Productivity and Nesting
Nesting timing
Egg measurements
Clutch Size
Survival and Longevity
Survival is shown as the proportion of birds surviving from one year to the next and is derived from bird ringing data. It can also be used to estimate how long birds typically live.
View number ringed each year in the Online Ringing Report.
Lifespan
Biometrics
Wing length and body weights are from live birds (source).
Wing length
Body weight
Ring Size
Classification, names and codes
Classification and Codes
- Order: Charadriiformes
- Family: Laridae
- Scientific name: Larus marinus
- Authority: Linnaeus, 1758
- BTO 2-letter code: GB
- BTO 5-letter code: GBBGU
- Euring code number: 6000
Alternate species names
- Catalan: gavinot atlàntic
- Czech: racek morský
- Danish: Svartbag
- Dutch: Grote Mantelmeeuw
- Estonian: merikajakas
- Finnish: merilokki
- French: Goéland marin
- Gaelic: Farspag
- German: Mantelmöwe
- Hungarian: dolmányos sirály
- Icelandic: Svartbakur
- Irish: Droimneach Mór
- Italian: Mugnaiaccio
- Latvian: melnsparnu kaija, kilens
- Lithuanian: balnuotasis kiras
- Norwegian: Svartbak
- Polish: mewa siodlata
- Portuguese: gaivotão-real
- Slovak: cajka morská
- Slovenian: veliki galeb
- Spanish: Gavión atlántico
- Swedish: havstrut
- Welsh: Gwylan Gefnddu Fawr
- English folkname(s): Land Gull
Research
Causes of Change and Solutions
Causes of change
The Great Black-backed Gull has not suffered the substantial declines in populations that have recently affected several other UK seabirds including coastal breeding Herring and Lesser Black-backed Gulls. It has been surmised that this species out-competes other species when scavenging for fishery discards and offal and therefore may continue to be able to benefit from these resources despite reductions in availability which have affected other species (Mitchell et al. 2004).
Publications (8)
Desk-based revision of seabird foraging ranges used for HRA screening
Author:
Published: 2019
A key step in understanding the possible impacts of a proposed windfarm development is to identify potential interactions between seabird breeding colonies and the proposed development areas. Such interactions are typically assessed using generic information on foraging ranges, derived from academic studies. This report uses the latest data to provide updated estimates of foraging range, which will help to ensure that the best available information is available when new developments are being considered.
01.12.19
BTO Research Reports

A review of the Biological Defined Minimum Population Scale (BDMPS) approach and methodology to apportioning non-breeding season impacts on seabirds arising from offshore wind farms
Author:
Published: 2025
Estimates of breeding seabird populations are used to assess the potential impacts of proposed wind farm developments. The approach used in these assessments is known as the Biologically Defined Minimum Population Scales (BDMPS) method, and it was developed by Furness in 2015. This report evaluates the methods developed by Furness, and highlights potential refinements to the current BDPMS approach, including methods, definitions, and data resources, to improve future ease of use and accuracy of estimates.
14.08.25
BTO Research Reports

The status of the UK’s breeding seabirds
Author:
Published: 2024
Five seabird species are added to the Birds of Conservation Concern Red List in this addendum to the 2021 update, bringing the total number of Red-listed seabird species to 10, up from six since seabirds were last assessed. The Amber List of seabirds moves from 19 to 14 species, and the Green List increases from one to two species.
29.09.24
Papers

Seabird Population Trends and Causes of Change: 1986–2023
Author:
Published: 2024
This report presents the latest seabird population trends in breeding abundance and productivity using data from the Seabird Monitoring Programme (SMP).The report documents changes in the abundance and productivity of breeding seabird species in Britain and Ireland from 1986 to 2023, and provides a detailed account of the 2021, 2022 and 2023 breeding seasons. This report includes both inland and coastal populations and trends from the Channel Islands, England, Isle of Man, Northern Ireland, Scotland, Wales and the Republic of Ireland, which are presented where sufficient data are available. The results from this report are used more broadly to assess the health of the wider environment, to inform policy and for conservation action.
21.11.24
Reports SMP Report

Reduced breeding success in Great Black-backed Gulls Larus marinus due to harness-mounted GPS device
Author:
Published: 2023
Great Black-backed Gulls can be negatively affected by harness-mounted GPS devices. This research reveals a reduction in breeding success among tagged birds compared to control groups.
13.06.23
Papers

Birds of Conservation Concern Wales 4: the population status of birds in Wales
Author:
Published: 2022
The latest review of the conservation status of birds in Wales. The report assessed all 220 bird species which regularly occur in Wales. There are now 60 species of bird on the Red List, with 91 on the Amber List and just 69 - less than a third of the total number of species - on the Green List. The latest review of the conservation status of birds in Wales comes 20 years after the first, when the Red List was less than half the length it is today. The report assessed all 220 bird species which regularly occur in Wales. There are now 60 species of bird on the Red List in Wales, with 91 on the Amber List and 69 on the Green List. The Birds of Conservation Concern in Wales report assesses the status of each species against a set of objective criteria. Data sources include the BTO/JNCC/RSPB Breeding Bird Survey and the BTO/RSPB/JNCC Wetland Bird Survey, as well as Bird Atlases and other BTO-led monitoring schemes and citizen science initiatives. These are used to quantify the changing status of the species’ Welsh population. The UK, European and global conservation status of the species is also considered, placing the Welsh population into a wider context. The Red ListSwift, Greenfinch and Rook – familiar breeding species in steep decline across the UK – are among the new additions to the Welsh Red List, which now also includes Purple Sandpiper, on account of a rapidly shrinking Welsh wintering population, and Leach’s Petrel, an enigmatic seabird in decline across its global range. These species now sit alongside well-known conservation priorities, such as Curlew, Hen Harrier and Turtle Dove as birds at risk of being lost from Wales for good. Uplands and woodlands Many of the species on the Red List are found in upland and farmland habitats. Starling, Tree Sparrow, Yellow Wagtail and Yellowhammer can no longer be found in much of Wales, while iconic species of mountain and moorland, such as Ring Ouzel, Merlin and Black Grouse, remain in serious trouble. Wales is well known for its populations of woodland birds; however, many of these – including Lesser Spotted Woodpecker, Willow Warbler and Spotted Flycatcher – also feature on the Red List. Goldcrest, which has seen its Welsh population shrink alarmingly in recent decades, is another new addition. On the coast The assessment for Birds of Conservation Concern Wales 4 took place before the impacts of avian influenza could be taken into account. Breeding seabird species have been struggling in Wales for many years, however, and most were already of conservation concern before the outbreak of this disease. Kittiwake, Puffin, Black-headed Gull, and Common, Arctic and Sandwich Tern remain on the Red List. Wales holds internationally significant numbers of breeding seabirds, making the decline of these colonies a global concern. The Amber ListDeclines in Wheatear, Garden Warbler and House Martin - all migrants which breed in Europe and winter in sub-Saharan Africa - mean these species have moved from the Green List to the Amber List. Many other ‘Afro-Palearctic' migrant species are also in decline, but the potential reasons for this, such as habitat loss and reduced availability of invertebrate prey, are not well understood. Closer to home, the declines in the Welsh Chaffinch population, linked to the disease trichomonosis, have seen the species Amber-listed. A number of other species have been placed on the Amber List because of the wider importance of their Welsh populations, which in each case make up more than half the UK total. Wales is home to more than three-quarters of the UK’s Choughs, for example, so recent declines are cause for concern. The nation’s breeding populations of Manx Shearwater, Pied Flycatcher, Goshawk and Hawfinch also account for more than half the UK total, as does its wintering population of Spotted Redshank. It’s not all bad news, though: some species now on the Amber List have moved up from the Red List, indicating some positive change in their population trends. These include Common Sandpiper, Great Black-backed Gull, Bullfinch, Goldcrest and Pied Flycatcher. The Green ListWhile the report contains much cause for alarm, several conservation success stories shine through. Red Kite was almost lost as a British bird during the first half of the 20th century, when only a handful of pairs remained in remote Welsh valleys. Since then, a sustained conservation effort has brought the species back from the brink. Wales is now home to more than 2,500 pairs of Red Kite and the species has now been moved to the Green List, reflecting this incredible change in fortunes. Song Thrush, Reed Bunting, Long-tailed Tit, Redwing and Kingfisher are among the other species to have gone Green, providing much-needed hope that things can go up as well as down.
06.12.22
Reports Birds of Conservation Concern

How high do birds fly? Development of methods and analysis of digital aerial data of seabird flight heights
Author:
Published: 2016
The purpose of this work was to develop a method for analysing digital aerial ornithology survey data, to derive species-specific flight heights. The focus of this work has been to develop an approach to analysis, rather than analysing a comprehensive dataset to derive generic flight height values. Although the project has been successful in developing such an approach to analysis, the BTO and Steering Group for the work emphasises that the values presented in this report are not intended to be used to inform assessments. Any party undertaking an ornithological collision risk assessment should seek advice from the relevant regulators and statutory nature conservation bodies on appropriate flight height values and avoidance rates to use. This report does not constitute such statutory advice.
16.03.16
BTO Research Reports

The avoidance rates of collision between birds and offshore turbines
Author:
Published: 2014
Report of work carried out by the British Trust for Ornithology in collaboration with the Environmental Research Institute on behalf of the Marine Scotland Science. Accurately estimating birds’ risk of collision with offshore wind turbines is a key part of the decision-making process for proposed renewable developments. However, the evidence base for quantifying the number of birds likely to avoid colliding with turbines is limited. Recent BTO-led work helping to fill this gap, improving the understanding of the impacts of offshore renewables on marine wildlife.
03.12.14
Reports Other reports

More Evidence
More evidence from Conservation Evidence.com
Partners
Citing BirdFacts
If you wish to cite particular content in this page (e.g. a specific value) it is best to use the original sources as linked in the page. For a more general citation of the whole page please use: BTO (20XX) BirdFacts Species: profiles of birds occurring in the United Kingdom. BTO, Thetford (www.bto.org/birdfacts, accessed on xx/xx/xxxx).